Acidophilic dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteria (DIRB) are now being detected in a variety of 'extreme' low-pH, radionuclide- and heavy-metal contaminated habitats where Fe(III) reduction is taking place, and may represent a significant proportion of metal-transforming organisms in these environments. Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5 is our model organism, a facultative iron-respiring Alphaproteobacterium. Strain JF-5 utilizes glucose as an electron donor with concomitant reduction of soluble and solid-phase Fe(III). Major findings of our research have been 1) Discovery of novel outer-membrane cytochromes c involved in iron respiration in JF-5, 2) Discovery of Cr(VI) reductase enzymes using both genomic and biochemical methods, 3) Development of enzyme detection methods specific for Cr-reducing enzymes, 4) Overexpression of cytochromes c in E. coli, and 5) Annotation of the Acidiphilium cryptum genome during an 'Annotation Jamboree' held at Idaho State University in August 2006. |
||
|
||
Acidiphilium cryptum JF-5

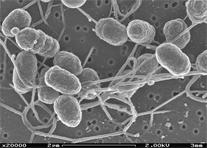 Electron micrograph showing connecting appendages. Image courtesy of Drs. Yuri Gorby and Alice Dohnalkova.
Electron micrograph showing connecting appendages. Image courtesy of Drs. Yuri Gorby and Alice Dohnalkova.